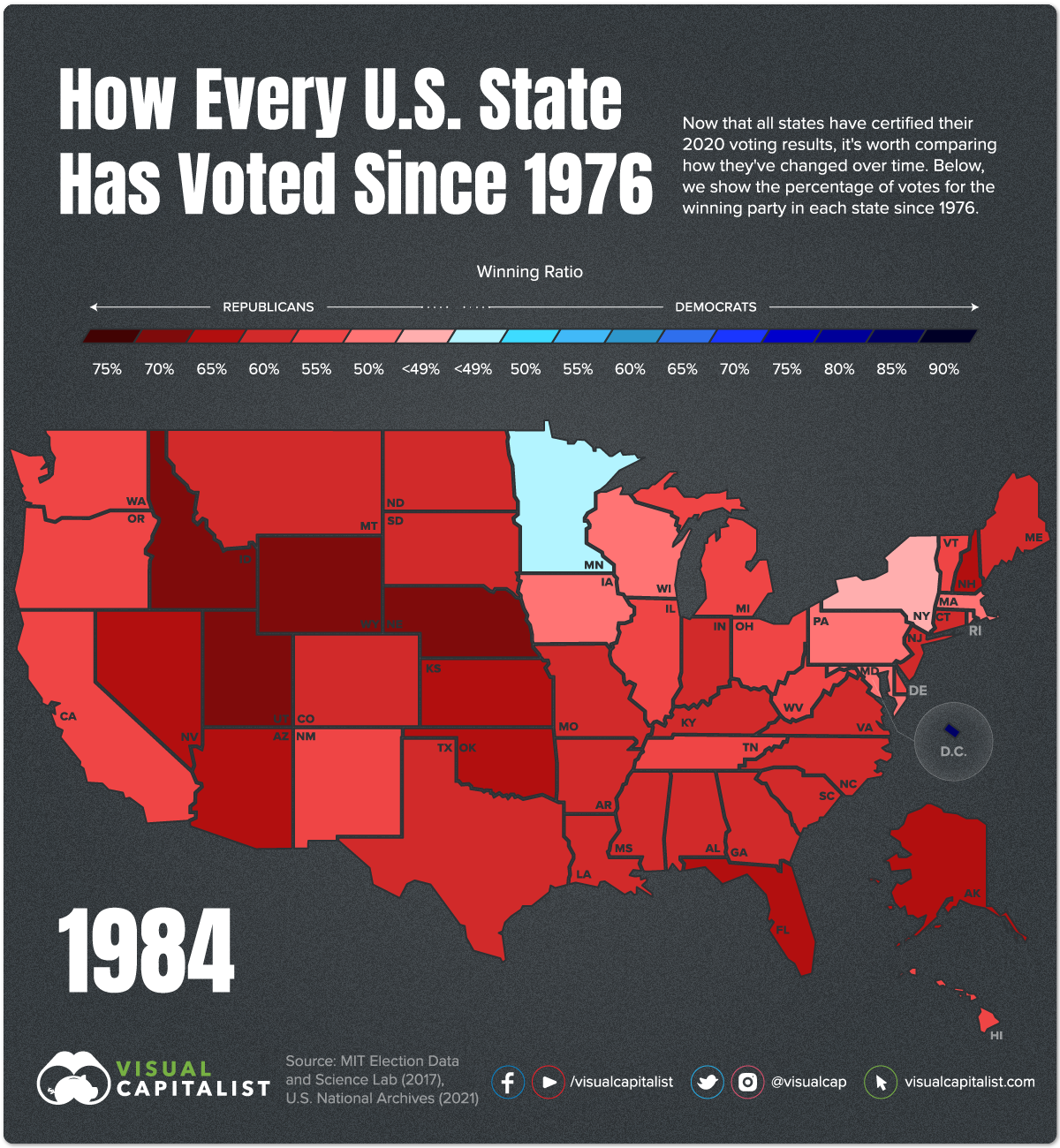
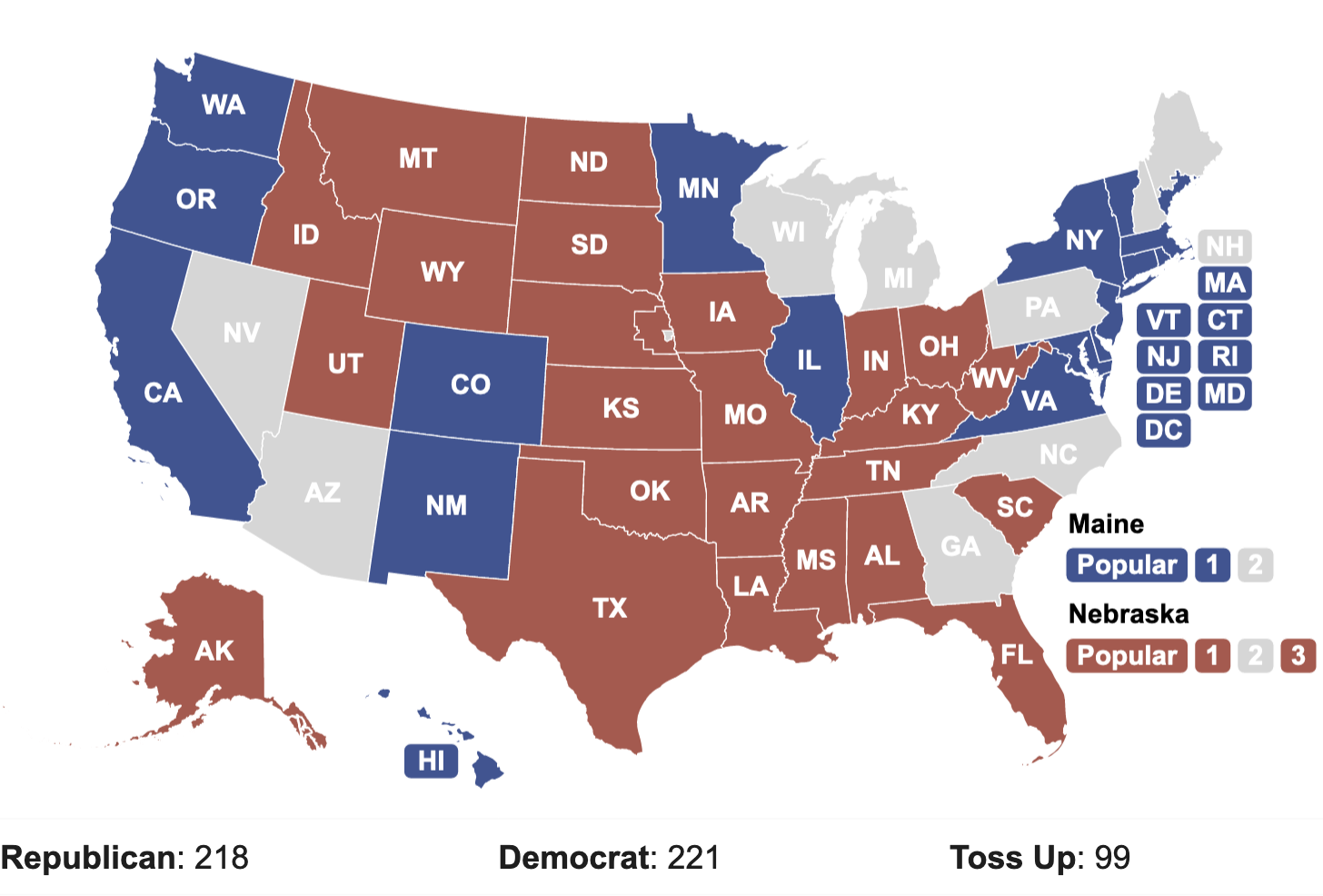
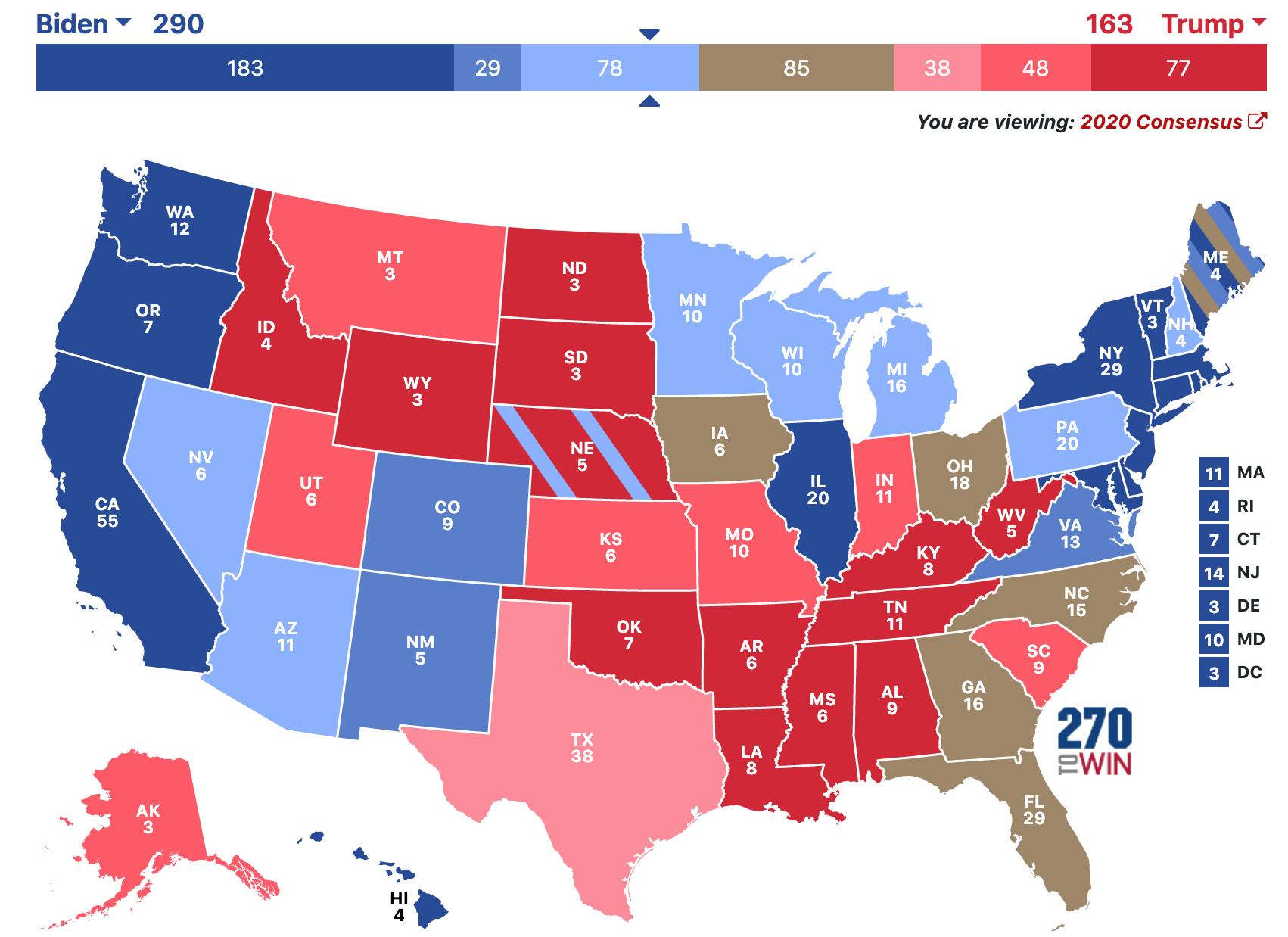
The electoral vote map plays a pivotal role in the United States presidential elections. It serves as the visual representation of how each state contributes to the selection of the president. Understanding this map is crucial for anyone interested in American politics or the democratic process.
Every four years, the United States undergoes a presidential election where the electoral vote map becomes a central focus. This map illustrates how the Electoral College system works and how each state's electoral votes influence the final outcome. For many, it is both a fascinating and complex aspect of American democracy.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore the intricacies of the electoral vote map, its historical significance, and its role in shaping modern elections. This article aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the electoral vote map, ensuring readers gain valuable insights into its functionality and importance.
Read also:Exploring The Life And Career Of Jon Knight
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Electoral Vote Map
- How the Electoral Vote Map Works
- Historical Significance of the Electoral Vote Map
- State Electoral Votes Distribution
- Understanding the Electoral College
- Swing States and Their Role
- Analyzing Past Election Results
- Impact on Modern Politics
- Criticisms and Controversies
- Future Trends and Predictions
- Conclusion
Introduction to the Electoral Vote Map
The electoral vote map is an essential tool in understanding the U.S. presidential election process. It visually represents how each state's electoral votes contribute to the selection of the president. Each state is allocated a specific number of electoral votes based on its population, and these votes are pivotal in determining the election's outcome.
This map has evolved over time, reflecting changes in population and political landscapes. By examining the electoral vote map, we gain insights into the dynamics of American politics and the strategies employed by candidates during their campaigns.
How the Electoral Vote Map Works
Electoral Votes Allocation
The allocation of electoral votes is based on the number of representatives each state has in Congress. Each state receives one electoral vote for every member it has in the House of Representatives and one for each of its two senators. For example, California, with its large population, has 55 electoral votes, while smaller states like Wyoming have just three.
- States with higher populations receive more electoral votes.
- Every state has a minimum of three electoral votes.
- The total number of electoral votes is 538, with 270 needed to win the presidency.
Winning the Presidency
To win the presidency, a candidate must secure at least 270 electoral votes. This system ensures that candidates focus on states with larger electoral vote allocations, leading to strategic campaigning. The electoral vote map highlights these key states and their significance in the election process.
Historical Significance of the Electoral Vote Map
The electoral vote map has a rich history dating back to the founding of the United States. It was designed to balance the power between larger and smaller states, ensuring that all states have a voice in the presidential election. Over the years, the map has witnessed numerous changes, reflecting shifts in population and political ideologies.
Read also:Unveiling The Life Of Paul Rudds Wife A Journey Beyond The Spotlight
Historical elections, such as the 1824 election where no candidate received a majority of electoral votes, and the 2000 election where George W. Bush won despite losing the popular vote, highlight the complexities and controversies surrounding the electoral vote map.
State Electoral Votes Distribution
Key States and Their Votes
Certain states, due to their large populations, hold significant influence in the electoral vote map. These include:
- California: 55 electoral votes
- Texas: 38 electoral votes
- Florida: 29 electoral votes
- New York: 28 electoral votes
These states often become battlegrounds during elections, with candidates investing heavily in campaign efforts to secure their electoral votes.
Understanding the Electoral College
The Electoral College is the system through which the president is elected. It consists of 538 electors, each representing a state's electoral votes. When voters cast their ballots, they are actually voting for these electors, who then cast their votes for the president.
This system ensures that smaller states are not overshadowed by larger ones, maintaining a balance of power across the nation. The electoral vote map visually represents the distribution of these electors and their votes.
Swing States and Their Role
Defining Swing States
Swing states, also known as battleground states, are those where the electoral outcome is uncertain. These states often determine the election's result due to their competitive nature. Examples include:
- Pennsylvania
- Michigan
- Wisconsin
Candidates focus heavily on these states, tailoring their campaigns to appeal to their diverse voter bases.
Analyzing Past Election Results
Examining past election results through the lens of the electoral vote map provides valuable insights into voting patterns and trends. For instance, the 2016 election saw Donald Trump securing a victory despite losing the popular vote, highlighting the map's influence on election outcomes.
Data from various sources, such as the Federal Election Commission and academic studies, support these analyses, offering a deeper understanding of the electoral process.
Impact on Modern Politics
Strategic Campaigning
The electoral vote map significantly impacts modern political strategies. Candidates focus on states with high electoral vote allocations and those considered swing states. This focus shapes campaign messaging, resource allocation, and voter engagement efforts.
Moreover, the map influences political party platforms, as they aim to address the concerns of voters in key states.
Criticisms and Controversies
The electoral vote map and the Electoral College system have faced numerous criticisms. Critics argue that it undermines the principle of "one person, one vote" and can lead to outcomes where the winner does not receive the majority of the popular vote.
Despite these criticisms, the system remains in place, with proponents arguing that it ensures a balanced representation of all states in the election process.
Future Trends and Predictions
As the United States continues to evolve demographically and politically, the electoral vote map will likely undergo changes. Predictions suggest that states with growing populations, such as Texas and Florida, will gain more electoral votes, while states with declining populations may lose votes.
Technological advancements and data analytics will also play a significant role in shaping future campaigns, allowing candidates to target specific voter groups more effectively.
Conclusion
The electoral vote map is a critical component of the U.S. presidential election process. It provides a visual representation of how each state contributes to the selection of the president and highlights the complexities and nuances of American democracy.
We encourage readers to engage with this topic further by exploring additional resources and participating in discussions about the electoral process. Your feedback and insights can help shape the future of democratic participation. Share this article with others and explore more content on our website to deepen your understanding of American politics.